Tuesday, April 30, 2024
< + > LLMs are not ready to automate clinical coding, says Mount Sinai study
< + > Nextech Supporting the Independent Ambulatory Practice
Independent clinical practices are in danger everywhere: if they don’t go out of business, large hospital chains tend to pipette them up. Bill Lucchini, CEO of Nextech, wants these independent practices to survive. Nextech’s EHRs and solutions for practice management and patient engagement software are highly specialized to Dermatology, Med Spa, Opthamology, Orthopedics, and Plastic Surgery in order to make it as efficient as possible.
In this video, Lucchini explains how Nextech addresses the pressures of being in private practice today. Besides tight staffing and tight reimbursements, the practices tend to depend on elective services and have to satisfy people who are used to the conveniences of online retail and delivery services. He cites a survey finding that 85% of patients would switch providers for convenience.
Transparency is another critical aspect of patient engagement. With higher deductibles, patients are concerned with how much treatment will cost and whether the benefits will be worth it. Plus, many of Nextech’s customers work with many patients who are doing elective procedures that are paid out of pocket.
Lucchini says that a generic EHR can’t map to the physician’s workflow; a specialized solution is needed for each discipline.
Generative AI is a part of their current offerings. With ambient voice recognition: their service fills in discrete fields of the medical chart while the doctor focuses on the patient. They also offer a virtual assistant for patient interaction and a special solution for street clinics called medspas. Check out this video to learn more from Bill Lucchini from Nextech.
Learn more about Nextech: https://www.nextech.com/
Listen and subscribe to the Healthcare IT Today Interviews Podcast to hear all the latest insights from experts in healthcare IT.
And for an exclusive look at our top stories, subscribe to our newsletter and YouTube.
Tell us what you think. Contact us here or on Twitter at @hcitoday. And if you’re interested in advertising with us, check out our various advertising packages and request our Media Kit.
< + > How AI-powered systems can help physician groups improve coding – and earn more
< + > Lean Digital: How AI Drives Treatment Recommendations for Weight Loss
The first article in this series laid out what we know about body weight and obesity today. The rest of the Lean Digital series will look at some contributions that digital technologies are making toward solutions.
The best contribution that information can make to weight management is to find more effective, personalized treatments: to match the right person to the right treatment, whether it be surgery, drugs, diet, exercise, or some combination. AI is turning up intriguing successes in this endeavor.
I talked to Dr. Ronald Razmi, co-founder and managing director at Zoi Capital and author of the book AI Doctor: The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare.
On the scale between automation and human intervention, Razmi is firmly on the side of the “human touch.” He says that the relationship between the care manager and the patient is the number one driver of success. But he approves of wearables to monitor people “in their natural habitat” and using data to personalize treatments.
Razmi identifies two general contributions of AI. First, it can accelerate research into genetics, microbiomes, and other factors to come up with a treatment plan. Second, AI can pull together medical data from disparate sources to create a unified patient record.
Genetics, Phenomics, and Biomarkers for Weight Gain
Razmi’s first approach characterizes the work of Dr. Andres Acosta, who did research into obesity biomarkers for years at the Mayo Clinic. He then cofounded Phenomix Sciences to commercialize their findings and allow them to be used “anywhere in the world.” He wants to move weight “from stigma to biology.” Not only does he hope to solve people’s weight problems; he wants to explain to them how they got where they are biologically.
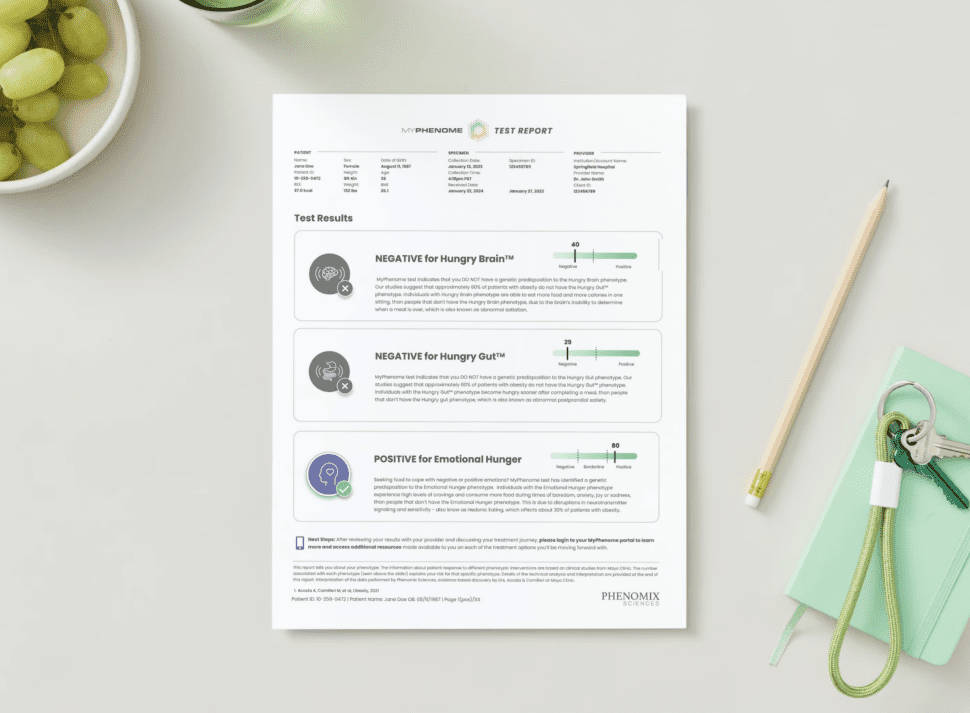
Not every obese person has the same problem, he says. Machine learning on biomarkers turned up 11 different classes of obesity—but that’s a rather complex classification. The researchers “took it out of the black box” and found that many of the classes had dimensions in common. Ultimately, they reduced the classes of obesity to four phenotypes, which were tested in a study:
- Hungry Brain: These people keep on eating because they don’t feel full, when others would. The solution includes intermittent fasting and eating a large volume of low-calorie foods such as salads.
- Hungry Gut: These people eat between meals, because something is telling the brain that the body needs something to digest. Treatment includes giving a protein hormone after each meal.
- Emotional Hunger: These people are using food compulsively to cover up negative emotions or feel a reward. The treatment is behavioral therapy.
- Slow Burn: These people might or might not be overeating, but the calories are not metabolized by the body and end up as fat. The treatment is exercise.
Biomarkers can also predict one’s response to medications. The Mayo team found some older drugs (which are cheaper than GLP-1 medications and have fewer side effects) that were rejected as ineffective, but that actually work on an impressive 30%-40% of patients.
If genetics lie at the basis of obesity, the patient is more likely to gain weight back after bariatric surgery.
Phenomix Sciences has marketed the MyPhenome Test to determine biomarkers and recommend treatments (Figure 1). Participants in the program in one study lost 8% of their weight in 12 weeks, compared to 4% in the control group.
Personalized and Holistic Behavioral Recommendations
OM1 illustrates an AI-driven approach to analyzing data from many sources. OM1 estimates risks and personalizes treatment recommendations by running large amounts of data on each patient through AI models. Their technology is based on real-world data from hundreds of millions of patients. NLP can extract details such as what treatments the patient has already tried, and their reactions.
Patients are evaluated on the contents of the EHR, pharmacy data, and claims data.
Like many companies profiled in this series, OM1 is holistic. They want to treat not just obesity or diabetes, but related comorbidities such as sleep apnea. Dr. Joseph Zabinski, their VP, head of commercial strategy & AI, says it’s important to decide what to treat. For some people obesity might be the chief complaint, whereas for others it might be diabetes, depression, or something else.
They also emphasize the interaction between mental and physical health. This interaction is still underestimated in most of the medical field, Zabinski says. He points out that some drugs might solve one problem but make depression or anxiety worse; on the other hand, a depression medication can lead to weight gain.
Besides injecting recommendations into the physician workflow, OM1 can do population-level studies and predictive modeling, where they identify people who might benefit from targeted treatment.
DarioHealth has been offering a digital solution for behavioral health for more than a decade. They, too, try to be holistic, according to Dr. Omar Manejwala, chief medical officer. At the start they might be treating obesity, but the solution can switch according to the patient’s needs and concentrate, say, on improving depression or back pain. AI is used in a modest way to match each person to the proper user journey.
Studies document Dario’s effectiveness for weight loss and diabetes, for reducing health care costs, and for cutting hospital readmissions.
A “whole person profile” is also important at apree health, according to CEO Donald Trigg. They can, for instance, flag when a drug might be inappropriate because of side effects or adverse interactions.
The company describes itself as “the first integrated health network that combines data-driven personalization, a coordinated care model, and aligned incentives,” and employs coaches certified by the National Board for Health and Wellness. Thus, they stress the human side of health care, striving to “create a durable primary care relationship” for behavioral health and care management. A blog posting lists their effects on improved outcomes.
Data points that they measure include the usual vital signs (blood pressure, A1C, etc.) along with other HEDIS metrics and related factors such as eye and kidney health, cancer screening, and depression.
In this article, we’ve seen a few uses for AI in weight treatments. Some verge on behavioral health. There will be a lot more on behavioral health as this series continues. The next article introduces the support that digital apps and services offer for behavior change.
< + > Nurses have a deep distrust of AI – but transparency and training could help
< + > Tennr Raises $18M in Series A Funding
Tennr, a NYC-based startup that automates manual work for healthcare organizations, raised $18M in Series A funding.
The round was led by a16z with participation from Foundation Capital and The New Normal Fund. Other investors (from the seed round) included YCombinator, Zaza Pachulia, Jennifer Kaehms, and other health and AI-focused investors.
The company, which has now raised over $25M, intends to use the funds to grow its team and scale its operations.
Co-founded by Trey Holterman, Diego Baugh, and Tyler Johnson, Tennr enables healthcare organizations to automate referral processing, payment posting, claims auditing, medical record management, and more. It cleans up the data coming in from faxes to automate patient intake and insurance communications. Tennr can read faxes, understand what information needs to be extracted from them, and where that information needs to go.
Commercial health plans like Prominence Health have begun to use the technology, among others.
Originally announced March 26th, 2024
Monday, April 29, 2024
< + > Lean Digital: How Apps and Services Can Help Control Weight
Is anyone not obsessed with weight? The health care field certainly is. Researchers have found ties between high body weight and an oversized list of unhealthy conditions. Payers have invested enormous amounts of money in decreasing individuals’ body weights. A Congressional bill would promote behavioral therapy for obesity and extend Medicare coverage for drugs treating obesity.
And yet weights continue to rise around the world, and the phenomenon starts at very young ages.
The rapidly expanding use of GLP-1 drugs has been life-altering for many, but brings its own disappointments: They’re extremely expensive, require continual use to be effective, have potentially negative effects on muscle mass, and are usually abandoned by patients. Paul T Jaeckel, a private practice dietitian at Paul Jaeckel Nutrition, warns that they tend to become “forever” medications.
Surgery is also expensive, with risks of its own, and its effects often don’t last.
In this series, we’ll feast on the contributions of digital technologies to weight control: remote monitoring and coaching, adherence support, genetic and phenotypic testing, nutritional advice, and more. These technologies can accompany or replace other medical interventions such as medications. I’ll also set a place at the table for activists who oppose the obsession with reducing weight and who call for obesity to be destigmatized. This first article in the series lays out what the medical field currently knows about weight.
Weighing the Problem of Obesity
Why is there a worldwide epidemic of obesity now, during the past 40 to 50 years? It comes from a convergence of several trends, according to leading public health and medical investigators. My interviewees came up with the same basic list.
First, there’s just more food available. Dr. Andres Acosta, Mayo Clinic researcher and co-founder of Phenomix Sciences, says that everyone but the richest people were undernourished for most of the duration of the human race, and that our bodies have evolved to eat as much as we can when we have the opportunity to do so.
Naturally, commercial interests are eager to capitalize on our predilections for large portions of highly processed foods with hidden salt and carbohydrates, as conveyed in this recent cartoon.
The tendency toward weight gain is also beset by sedentary jobs, sedentary leisure activities (notably television and video games), sweetened beverages, decreased sleep, and social isolation.
In short, our world is easier and more fun to live in, and we are hard-wired to take advantage of it.
Research has established a strong genetic component to one’s weight. Other factors that enter into weight, besides what we traditionally call “will power,” include:
- Changes that hormones, age, smoking cessation, and other factors make to our metabolism and therefore how the body handles calories
- Emotional needs for comfort and relief from stress
- Cultural factors, such as what one’s relatives expect one to eat
- Environmental factors, such as the availability of fruits and vegetables versus fast food restaurants in one’s neighborhood, or whether streets have sidewalks and are safe to walk on
- Stresses, including lack of sleep and lack of time to prepare healthy, well-balanced meals
Dr. Kate Behan, chief medical officer of Arcadia, cites several examples of social determinants of health that are relevant to weight: access to healthy foods, and limited ability to exercise due to cramped housing, unsafe neighborhoods, and communities without public spaces that promote exercise.
True hunger is creeping back to many threatened regions of the world, usually caused by wars and disrupted supplies. But the phenomenon of plenty, not deprivation, is more prominent at this time.
A Dissenting View on Body Types
Our society is certainly obsessed with weight. So are many other societies, and as American views of health and fashion spread—and as these societies get heavier too. But a protest movement against the negative perceptions of fat has also arisen.
This protest movement, inspired by the movements against racism, sexism, homophobia, etc., tells people to accept fatness and obesity. Some people talk of “fat pride.”
Certainly, there is plenty of evidence that people of greater weights suffer from discrimination and abuse. The medical profession itself is rife with improper handling of the many people whose weight is much greater than the medically recommended limits.
Gradually, alert researchers and doctors have adopted a more nuanced view of weight and strategies to change it. An important turning point was a 2005 study in JAMA published by a team led by Katherine Flegal of the Centers for Disease Control. Flegal showed that obesity was not strongly associated with increased morbidity, throwing into doubt the value of the sometimes extreme treatments that are often recommended.
Some advocates for the obese raise objections against what they call the “medicalization” of this condition, just as people with some psychological conditions are now doing. Some feel that obesity shouldn’t be treated as a problem at all; that the problem is how people view the obese. Other advocates want weight handled as a lifestyle issue that each person themselves should choose how to handle.
A recently released book that explores Flegal’s impact, as well as many other psychological, historical, and sociological themes, is Unshrinking: How to Face Fatphobia by philosopher and social activist Kate Manne. She places body size in a cultural and historical context that may stretch many readers’ thinking, and I recommend the book to medical professionals as well as the general public. I won’t try to summarize her many points, but I’ll note that she ignores some problems known to be caused by fatness, such as the effect of heaviness on knees and backs.
We’ll see in this series that the medical profession and health researchers are beginning to align with the views of the fat activists, while continuing to try to reduce weight. Sophisticated researchers and clinicians understand that reducing weight is not a simplistic matter of reducing calories and increasing exercise. Society is increasing “medicalization” in some ways through the growing use of surgery and drugs, but decreasing it in other ways by improving behavior interventions and using digital IT to help people stick to regimens more easily.
Sara Shanti, a partner specializing in health care at law firm Sheppard Mullin, says that many practitioners are using the terms “weight health” or “body health” instead of “weight loss.” And you might note that this series avoids the term “overweight,” because it implies that there are good weights and bad ones.
What Have GLP-1 Medications Accomplished?
GLP-1 medications have been prescribed to control diabetes over the past ten years, but only recently did studies show they have an effect on weight as well. They might be something of a miracle drug, with potential even for reducing addictions and Alzheimer’s symptoms, perhaps even Parkinson’s disease. Two relatively recent GLP-1 drugs, Tirzepatide and Semaglutide, were shown to be particularly effective in a recent study.
But like most drugs, GLP-1 medications have serious downsides. They cost more than $1,000 per month. The medications have serious, unpleasant side effects, causing most to go off the drugs early for a variety of reasons. Furthermore, people who go off the drugs have a high probability of regaining the weight they lost—a problem that the digital solutions in this series can help with.
Yet the potential of GLP-1 drugs to reduce health care costs related to obesity are attracting coverage from more and more payers.
Arcadia has done research on disparities in GLP-1 treatment for diabetes among Medicare patients, which mirror familiar problems in other areas of health care. Behan says, “Usage of GLP-1s in affluent areas is 6% higher in aggregate than other areas. When accounting for diabetes prevalence between these two populations, the disparities are intensified. Our analysis found that affluent areas have a 28% higher rate of GLP-1 fills per 1,000 diabetics than elsewhere. Analysis of other populations, such as Medicaid recipients, would likely reveal even greater disparities.”
In the following articles of the series, we’ll look at how digital interventions are making verifiable improvements in weight-related goals. The next article shows how precision medicine, powered by AI, can help choose the right approach to weight control.
< + > Brightside Health Raises Strategic Series C, Welcomes Trip Hofer to Board of Directors
With Over $100M in Total Funding, the Telemental Health Company is Poised for its Next Phase of Growth
Telemental health company Brightside Health today announced a strategic Series C raise led by S32, as well as the appointment of industry titan Trip Hofer to the Board of Directors to advise on go-to-market strategy and execution. This news builds on the company’s recent momentum, including new and expanded payer partnerships to support Medicaid and Medicare lives and notable results for its award-winning Crisis Care program for individuals with elevated suicide risk.
Brightside Health serves people with mild to severe clinical depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders, including those with elevated suicide risk, through precision psychiatry, clinically proven therapy, and Crisis Care. The impressive activity and results attracted lead investor S32, along with Kennedy Lewis, Time BioVentures, and Anne Wojcicki (Redwood Pacific). Existing investors ACME, Mousse Partners, and Triventures also contributed to the raise of $33M, an intentional amount that will be used to fuel Brightside Health’s growth into new markets and new offerings. All of this comes at a critical time for the country as one in five adults live with mental illness, such as anxiety or depression.
“Brightside Health is on an exciting trajectory, and S32 is thrilled to support their mission to make mental healthcare more easily accessible to everyone,” said Mike Pellini, MD, General Partner at S32. “The company is well-positioned to expand their offerings with Medicare, Medicaid, and other underserved populations while partnering with payers and providers to deliver measurably better outcomes.”
Since its $50M Series B in November 2021, Brightside Health has made significant developments, building programs for individuals with severe mental health conditions, expanding to new underserved markets, publishing close to a dozen peer-reviewed research papers, and deepening its leadership bench. Brightside Health has also continued to appoint advisors and reputable industry leaders to its Board of Directors to support aggressive yet attainable goals to scale, the latest of which includes Hofer, whose deep experience in the payer market will further strengthen Brightside Health’s go-to-market initiatives and execution.
“I’m honored to be joining Brightside Health’s Board of Directors as the company reaches this impressive milestone,” said Trip Hofer, Brightside Health Board Member and former CEO at Optum Behavioral Health Solutions. “Their proven track record in high-quality care delivery and meaningful growth over the past few years indicate that Brightside Health has found their distinct competitive advantage. I look forward to leveraging my experience to advise them on opportunities that will help them effectively scale while maximizing impact for patients and payers alike.”
Brightside Health’s services are available for commercially insured and cash-pay patients in all 50 states as well as Medicaid and Medicare beneficiaries in select states. In fact, Brightside Health recently announced an expansion with payer partners including CareOregon, Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Texas, and Centene. With this Series C funding, the organization’s leadership continues to chart plans for additional expansions.
“We’re thrilled to announce this raise and simultaneously welcome Trip, an incredible industry thought leader, to help propel Brightside Health into the next phase of our growth,” said Brad Kittredge, Co-Founder and CEO at Brightside Health. “These major steps forward enable us to accelerate our expansion into Medicare, Medicaid, and beyond, while deepening our advantage with technology and AI to deliver the best outcomes in the industry. This investment aligns with our continued focus on capital-efficient enterprise value creation, putting us on a comfortable path to profitability while further advancing our goals and mission.”
For more information on Brightside Health, visit brightside.com.
Originally announced March 26th, 2024
< + > Digital from the start: New medical campus to rise in Singapore's east
Sunday, April 28, 2024
< + > Bonus Features – April 28, 2024 – 22% of employers fully trust chronic condition management vendors, Common Agreement v2.0 requires support for FHIR API exchange, plus 29 more stories
Welcome to the weekly edition of Healthcare IT Today Bonus Features. This article will be a weekly roundup of interesting stories, product announcements, new hires, partnerships, research studies, awards, sales, and more. Because there’s so much happening out there in healthcare IT we aren’t able to cover in our full articles, we still want to make sure you’re informed of all the latest news, announcements, and stories happening to help you better do your job.
News
- ONC released Common Agreement 2.0. Updates that require support for FHIR-based APIs should allow TEFCA participants to more easily exchange information directly, and enable individuals to more easily access their own information.
- Only 22% of companies offering chronic condition management solutions to employees fully trust vendors to act in the employer’s best interest, according to a Quantum Health report. In other news, Quantum Health launched Premier Oncology, a cancer care navigation tool.
Partnerships
- GE HealthCare expanded its partnership with Elekta, a precision radiation oncology vendor.
- RCM outsourcing vendor Ensemble Health Partners expanded its partnership with Microsoft.
- DrFirst announced a partnership with PatchRx, a medication adherence company.
- Specialty telemedicine vendor Thirty Madison is partnering with Talkspace to expand mental health support for women.
- Operations software vendor symplr integrated with Branch, a workforce payments platform.
Products
- Augmedix launched Augmedix Go, ambient AI medical documentation for the ED, and announced HCA Healthcare as a pilot user.
- Clinical data exchange vendor MRO is now automating data exchange between providers for continuity of care purposes.
- Patient engagement and payment vendor RevSpring updated IVR Advantage to include prescription refill requests and status inquiries.
- Interoperability vendor Innovar Healthcare released an OSS Mirth Connect plugin that’s now available on AWS Marketplace.
- Truveta released a mother-child EHR dataset to drive research from pre-pregnancy through childbirth and pediatric care.
- Risk management vendor CorVel unveiled a data and service hub for its customers in managed care.
- Senior virtual care vendor Connect America launched a fall prevention program.
- OMNY Health launched real-world data and evidence solutions for gastroenterology and announced more than 5,000 GI providers are in its research network.
- Anatomy IT expanded its Security Suite to align with NIST’s five core cybersecurity functions.
Sales
- Cohere Health and Humana expanded their prior authorization partnership to include diagnostic imaging and sleep services.
- Texas-based FQHC Coastal Bend Wellness Foundation selected eClinicalWorks AI solutions and Sunoh.ai. In addition, Texas-based Brownfield Regional Medical Center implemented Sunoh.ai.
- Indiana-based Community Health Network selected Biofourmis to scale care-at-home services.
- Maryland-based Anne Arundel Dermatology expanded its partnership with Relatient to include scheduling.
- Houston Methodist expanded its deployment of BioIntelliSense‘s BioButton continuous patient monitoring solution.
Company News
- FDB announced its FDB Targeted Medication Warnings solution earned a Toolbox designation from Epic and is now available in the Epic Showroom.
- Boston’s Brigham and Women’s Hospital is conducting a research study with FeelBetter, maker of patient management technology for patients taking many medications.
- Wisconsin-based Chorus Community Health Plans is saving $2.6 million annually using Foodsmart food benefits management and nutrition planning.
- National Institutes of Health added SAS Viya to the All of Us researcher workbench, enabling more than 9,500 participating researchers to access SAS Analytics Pro.
- NextGen passed Health Resources & Services Administration synthetic data testing requirements for UDS+ reporting for FQHCs and community health centers.
People
- Medicare ACO Vytalize Health appointed Sherry Slick as Chief Information Officer and Charles Colligan as Chief Financial Officer.
- Health information network Availity appointed Sean Barrett as Chief Product Officer.
- Kidney care management company Interwell Health appointed Clark Curtis as Chief People Officer.
- Acute virtual nursing vendor AvaSure appointed Paula Cobb as Vice President of Marketing.
- Ambient AI documentation vendor DeepScribe added Dr. Miles Snowden to its advisory board.
If you have news that you’d like us to consider for a future edition of Healthcare IT Today Bonus Features, please submit them on this page. Please include any relevant links and let us know if news is under embargo. Note that submissions received after the close of business on Thursday may not be included in Bonus Features until the following week.
Saturday, April 27, 2024
< + > Weekly Roundup – April 27, 2024
Welcome to our Healthcare IT Today Weekly Roundup. Each week, we’ll be providing a look back at the articles we posted and why they’re important to the healthcare IT community. We hope this gives you a chance to catch up on anything you may have missed during the week.
NextGen’s Investments in Mobile, Cybersecurity, and Interoperability. Colin Hung had a chance to briefly chat with NextGen CEO David Sides. Their conversation touched on Ambient Assist in the mobile EHR, making Mirth Connect GDPR compliant, and partnering with CrowdStrike on zero trust. Read more…
How AI is Shaping Drug Discovery. John Lynn connected with Mati Gill at AION Labs. They discussed how AI can expedite the discovery of new drugs, along with why it helps to bring together the best AI professionals and experts from pharmaceutical companies. Read more…
International Hospitals Investing in Portals and Digital Front Doors. Colin talked to Everton Santos at KLAS Research about the firm’s Global Patient Engagement 2024, which found patient centricity is becoming more prevalent in regions like the EU and Asia – and WhatsApp is the name of the game in the developing world. Read more…
CIO Podcast: Health IT Project Management. John heard from Michael Restuccia at Penn Medicine about what occupies the most time for today’s CIOs. They also touch on the role of AI and telehealth in the organization. Read more…
Balancing Digital Transformation and Regulatory Compliance for Patient Security. There are more than 50 lawsuits targeting hospitals for improper use of third-party tracking technology. Providers must partner with vendors demonstrating an established compliance record, said Michelle Berryman at Hero Digital. Read more…
A Guide to Proactive Healthcare Cybersecurity. To protect against breaches, Troy Hawes at Moss Adams recommended identifying where the biggest weaknesses are, where a breach could occur, and proactively working toward strengthening those gaps. Read more…
Leveraging AI to Address the Mental Health Crisis. AI-powered avatars and voice agents are increasing access to mental health assessments without substantially increasing personnel costs, according to Raj Tumuluri at Openstream.ai. Read more…
Exchanging, Managing, and Meaningfully Using Health Data in 2024. Jolie Ritzo outline how Civitas Networks for Health is standardizing SDOH data, harnessing AI, and promoting consent management in alignment with the needs of its member organizations. Read more…
Health Data Sharing Impacts How Clinicians Care for Patients. Dr. Guillermo Diaz at the Los Angeles Department of Health Services and Ali Modaressi at LANES described why data sharing advancement is more than a policy or technological discussion. Read more…
This Week’s Health IT Jobs for April 24, 2024. This week’s listings include lots of roles for professionals with MEDITECH expertise, along with positions in medical billing and coding. Read more…
Bonus Features for April 21, 2024. 89% of physicians said generative AI vendors need to be transparent about where info comes from, 73% of consumers expect a 4-star rating before they’ll engage with a provider. Read more…
Funding and M&A Activity:
- Precision medicine AI vendor Zephyr AI raised $111 million in Series A financing.
- Hippocratic AI raised $53 million in Series A funding and announced the latest phase of testing for its generative AI-powered agents for non-diagnostic, patient-facing services.
- Service provider Sagility acquired BirchAI, maker of generative AI software for healthcare call centers.
- Process automation vendor Syllable acquired Actium Health, which developed the CENTARI platform to predict a patient’s likelihood of needing specific medical services.
Thanks for reading and be sure to check out our latest Healthcare IT Today Weekly Roundups.
Friday, April 26, 2024
< + > 40% of people in Europe face challenges with digital literacy
< + > The Balance Between Digital Transformation and Regulatory Compliance for Patient Security
The following is a guest article by Michelle Berryman, FIDSA, Executive Creative Director at Hero Digital
Patient privacy is the foundation of our healthcare system. Ensuring trust in the confidentiality and security of sensitive health information enhances patient care effectiveness and puts individuals at ease to seek care.
However, the integration of digital technologies in healthcare introduces new challenges in privacy protection. While tracking technologies like cookies and pixels offer benefits in data gathering for improved user experience and analytics, they also pose risks to patient privacy, potentially exposing sensitive health information without explicit consent.
Recognizing these risks, the Office of Civil Rights at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has issued clear guidelines for HIPAA-covered entities. These guidelines emphasize the importance for healthcare organizations to regulate their use of digital tracking technologies to comply with HIPAA regulations, which set standards for protecting patient data through appropriate security measures against unauthorized access or disclosure.
For providers, ensuring regulatory compliance is crucial. I’ll outline steps they can take to navigate these challenges when it comes to their digital experience.
The Costs of Failing to Comply
The world of patient-tracking technologies in healthcare is fraught with significant risks, as evidenced by recent legal repercussions.
Since August 2022, the legal landscape has been increasingly challenging for healthcare providers utilizing third-party tracking technology. BakerHostetler, a legal firm, has documented more than 50 lawsuits targeting hospitals for improper use of third-party tracking technology. These legal actions often stem from the discovery that tracking technologies were transmitting sensitive patient data to large tech firms, including Meta and Google, without appropriate consent.
To cite one example, several Louisiana hospitals, including major healthcare networks like LCMC Health Systems and Willis-Knighton Health System, are facing class action lawsuits due to online tracking technologies, such as pixels, that may have shared protected health information without consent.
Another vivid and personal example of these risks was experienced by one of my clients. The potential for violation was so alarming that they made the decision to completely disable their site analytics. This drastic step was taken to mitigate the risk until we could provide a solution, which came in the form of implementing a HIPAA-compliant setup using Adobe Customer Journey Analytics combined with Health Shield. We made sure their analytics practices were both safe and compliant.
Tech companies are a big part of the story. Meta is facing an ongoing lawsuit for allegedly scraping health data from hundreds of hospital websites with its Meta Pixel Helper, which is used by thirty-three of the top 100 hospitals in the U.S. The allegations included the unauthorized collection of highly sensitive protected health information (PHI) such as medical conditions and appointment details, which were linked to users’ unique IP addresses.
Accessibility is another issue to weigh carefully. In March, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) emphasized the importance of language services in healthcare access and outcomes, highlighting the necessity for states to meet the language needs of their communities.
The review was initiated in response to allegations that individuals with limited English proficiency in 19 states were not provided meaningful language access to COVID-19 services, in violation of Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Over 10,900 state agencies and their subrecipients received technical assistance letters and training materials to remind them of their obligations under Title VI.
The importance of patient convenience, experience, and security will only grow in the coming years. The question is, how can it be done while protecting patient data and preserving the digital experience between patient and provider?
Analyzing Third-Party Vendors and Digital Solution Options
In light of the HIPAA regulations, healthcare providers are urged to partner exclusively with third-party analytics vendors boasting established compliance records with privacy regulations, and it’s essential to confirm vendors’ possession of Business Associate Agreements (BAAs), which ensures adherence to HIPAA rules.
This adherence empowers providers to utilize data analytics effectively, improving patient care, operational efficiency, and decision-making while staying compliant with the latest regulations from the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). This approach helps organizations navigate regulatory changes and foster a culture of privacy and trust within the healthcare sector.
Google and Adobe are the most commonly used analytics platforms.
In the past, Google Analytics was not advisable for most providers due to Google’s refusal to engage in a BAA, thereby contravening regulations delineated in the original HHS bulletin. However, in the latest bulletin, the HHS clarifies their stance. Providers can use Google Analytics if they sign a BAA with a vendor to ensure data will be properly safeguarded before sending it to Google.
If you don’t sign a BAA, using Google Analytics comes with big risks. Under certain conditions, the most recent bulletin explains, tracking technologies used on a regulated entity’s webpage can access personal health information. This applies to pages that allow people to schedule appointments or use a symptom-checker tool without entering credentials.
This is another area to be worried about if you’re using Google. Why? It’s critical that whatever anonymized data is sent cannot be, through creative means, tied back to an individual’s past, present, or future health, healthcare, or payment for healthcare.
Adobe Analytics does not inherently comply with HIPAA standards. Nevertheless, Adobe offers HIPAA-ready services like Healthcare Shield, incorporating a real-time customer data platform. These services involve additional costs and necessitate a BAA between Adobe and the customer.
Beyond these two, there are numerous HIPAA-ready solutions, such as Mixpanel, Plausible, Freshpaint, and Piwik Pro, which offer diverse features and compliance levels.
- Mixpanel delivers robust reporting and data visualization.
- Plausible stands as an open-source, self-hosted alternative.
- Freshpaint guarantees HIPAA compliance throughout its entire technological infrastructure, enabling clients to persist with Google Analytics usage.
- Piwik Pro adheres to all privacy regulations, including HIPAA, and provides varied data storage options.
Getting with your legal and compliance teams to talk through the best fit for your organization is always a recommended best practice.
Next Steps for Providers Wanting to Ensure Compliance and Data Security
It’s essential for healthcare companies to recognize that navigating this intricate and ever-changing landscape alone is not necessary. Adopting a proactive stance tends to prove to be the more successful strategy.
Given the complexity of healthcare regulations and the evolving nature of digital threats, it may be wise to consult with a digital experience agency with a track record of working with healthcare organizations. A tailored, expert-driven approach can help ensure that your organization not only meets current regulatory standards but is also prepared for future challenges.
Choosing the right partner is a significant decision given the potential legal consequences of non-compliance, so it’s crucial to evaluate your options carefully. Agencies such as Hero Digital can help implement tracking changes or full-scale implementations with your organization and legal teams.
With your security locked down, decision-makers are free to invest in and focus on improving overall digital experiences. Enhanced digital experiences lead to more accessible patient services and, ultimately, superior patient outcomes.
By securing patient data and ensuring compliance, healthcare providers can concentrate on what truly matters—delivering exceptional patient care without the constant worry over data privacy issues.
 About Michelle Berryman
About Michelle Berryman
Michelle Berryman, FIDSA, serves as the Executive Creative Director at Hero Digital. Michelle has over two decades of experience as a User Experience Designer and Digital Strategist with a significant background in industrial design, user-centered design, research, innovation, experience strategy, and brand management. She believes in the power and elegance of simplicity and that interactions should be authentic, meaningful, and pleasurable. She strives to make an emotional connection with users by eliciting desire and delight with the interfaces she designs. In 2015, she was named one of the Top 50 Industrial Designers of the last 50 years by the Industrial Designers Society of America. Her specialties include Digital Strategy, Innovation, Interaction Design, User Experience, Information Architecture, User Research, Corporate Identity, Project Management, Business Development & Emerging Technologies. When she’s not designing, she can be found traveling the world, camera in hand, looking for beauty, inspiration, and fresh perspectives.
< + > Sagility Acquires BirchAI, a GenAI Company in the Healthcare Space
Sagility to Transform Member, Patient, and Provider Interactions Using BirchAI’s SaaS Platform
Sagility LLC, one of the leading technology-enabled services providers in the healthcare services space, announced its acquisition of Seattle-based BirchAI. BirchAI is a healthcare technology company offering cloud-based, GenAI call technology built by experts in transformer-based natural language processing. BirchAI enables clients to reduce operational costs by providing various AI-powered real-time customer support solutions to manage complex healthcare transactions.
Ramesh Gopalan, Sagility’s Group CEO noted, “We’re thrilled to announce this acquisition of BirchAI, which enables Sagility to build on our healthcare domain expertise and demonstrates our commitment to technology-enabled transformation of the healthcare value chain. BirchAI’s generative AI capabilities will help us deliver significantly more impactful ROI to our clients.”
With this acquisition, Sagility broadens its analytics and automation-backed healthcare engagement services that it provides to large national payers, Blues plans, regional payers, health systems, medical devices, and other healthcare providers.
BirchAI will further propel Sagility’s delivery of healthcare operations, enhance the member and provider experience, and improve quality of care. “Sagility brings strong domain expertise and a renowned healthcare presence to complement our generative AI solutions,” noted Kevin Terrell, Co-Founder and CEO at BirchAI.
Sherman & Company served as BirchAI’s financial advisor on the transaction.
About Sagility
Sagility combines technology and transformation-driven healthcare services with decades of healthcare domain expertise to help clients draw closer to their customers. The company optimizes the entire member/patient experience through service offerings for clinical operations, member engagement, provider solutions, payment integrity, claims cost containment, and analytics. Sagility has more than 34,000 employees across 5 countries.
Visit sagilityhealth.com to learn more.
About BirchAI
BirchAI is a GenAI company founded in 2020 by Kevin Terrell, Sumant Kawale, and Yinhan Liu. The concept was developed through Seattle’s AI2 Incubator, one of the world’s leading supporters of AI-first startups.
BirchAI helps their clients reduce average handle time by up to 35% by automating complex healthcare interactions using proprietary speech-to-text and Large Language Models that efficiently integrate with most commonly used CCaaS and CRM solutions.
Visit birch.ai to learn more.
Originally announced March 26th, 2024
Thursday, April 25, 2024
< + > To find success with AI, health IT leaders must understand its recent evolution
< + > Guide to a Proactive Healthcare Cybersecurity Stance
The following is a guest article by Troy Hawes, Managing Director at Moss Adams
The recent cybersecurity attack against Change Healthcare caused dramatic disruptions to one of the nation’s largest prescription processors.
On the morning of February 21, 2024, a ransom group, BlackCat, directed a cyberattack at Change Healthcare, owned by healthcare conglomerate UnitedHealth. The attack kept Change Healthcare’s systems down for three weeks, even prompting the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to deploy accelerated payments and loan programs for healthcare organizations affected by the attack, akin to the support deployed during the pandemic.
The attack sparked a long overdue conversation about how organizations in the healthcare industry are financially impacted by these attacks, what these attacks can look like, and how to be proactive against them.
The Cost of a Cybersecurity Breach
Cybersecurity at its core is a way to protect valuable data and personal identifiable information (PII), such as credit card information, social security numbers, tax records, and more. For a healthcare entity, the data and information are viewed as extremely valuable as it includes PII as well as other health information that can be used for insurance fraud and identity theft.
Consequently, the healthcare industry has a large target on their backs as the data housed by health organizations is extremely valuable for malicious actors. The data is also necessary in order to maintain services to patients, so when a cybercriminal uses ransomware and makes that data unavailable, healthcare entities struggle to provide necessary care for patients.
The cost of allowing a data breach to occur can cause an exponential financial impact on an organization. According to the 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report from IBM and the Ponemon Institute, the average data breach cost a healthcare organization around $10 million. For a healthcare entity, this number could drastically change, depending on the impact of the attack. A large-scale cyberattack, like the Change Healthcare attack, could cost an organization 10 times more than average. Recent examples include Tenet Healthcare’s cyberattack in 2022, which reportedly cost them over $100 million, and CommonSpirit Health’s 2022 cyberattack that reportedly cost them $160 million.
While we won’t know the total financial impact of the Change Healthcare cyberattack for some time, we can assume that the $22 million ransom payment the healthcare organization apparently made will be a fraction of the financial hit they will take as a result of the attack.
Dissecting a Cyberattack
Unfortunately, malicious actors haven’t had much of a problem attaining access to healthcare systems. As of mid-March, 117 other healthcare organizations have experienced a cybersecurity breach in 2024, potentially affecting around 13 million patients, according to the HHS.
So, why is it easier for healthcare organizations to be breached?
Often, it’s due to the number of entry points into the organization that come from medical devices and other Internet-connected devices, use of outdated systems, a lack of cybersecurity education and awareness, and inadequate security budgets. Malicious actors take advantage of these weaknesses by cycling through different methods to retrieve valuable healthcare data, often using social engineering tactics to manipulate healthcare practitioners into divulging confidential or personal information they can use to break into systems.
With the introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity, these attacks and tactics are becoming more sophisticated and difficult to mitigate. AI changes the way malicious actors target organizations, drastically shifting the cybersecurity landscape.
AI-powered tools allow attackers, for example, to not only generate phishing emails that more closely resemble real-world scenarios for healthcare workers to fall susceptible to, but the technology allows bad actors to do it more, at scale, better, and faster. As such, AI-generated attacks are harder to identify. Hackers also utilize AI to quickly collect and analyze the data and information they steal, making it easier for them to sort out the datasets and sell them on the black market or hold them for ransom.
Regrettably, AI-based cyberattacks pose a large threat to an already vulnerable healthcare industry. Organizations can, however, leverage AI to fight back.
Building a Proactive Cybersecurity Stance
Part of a renewed strategy to keep organizations protected is through proactive cybersecurity. Too often healthcare organizations use a more reactive cybersecurity stance – choosing to focus more on fixing a breach when it occurs rather than anticipating vulnerable systems and trying to prevent attacks.
Healthcare organizations can better protect themselves by shifting to a more proactive cybersecurity stance – centering efforts on identifying where the biggest weaknesses are, where a breach could occur, and proactively working towards strengthening those gaps. For a healthcare organization, those gaps typically lie within outdated systems and the number of network-connected devices.
To build a proactive stance, it is important for an organization to conduct risk assessments to know where its biggest weaknesses and holes could be. Cybersecurity risk assessments and analysis should be conducted at least annually and it should identify all assets that may process, store, or transmit sensitive data so that they can be secured.
Third-party security assessments and penetration testing can allow experienced security consultants to assess systems to find where potential holes in security exist and provide recommended remediation actions. Tools, such as extended detection and response, and similar solutions, collect and correlate data across all systems and provide proactive alerts and mitigation activities that are essential tools for a proactive response to threats.
Healthcare organizations can also employ their own AI-powered tools, such as predictive analytics, threat detection, and response systems to help proactively protect patient PII. These tools use AI algorithms to detect and identify potential threats before they emerge. As AI algorithms continue to improve over time, AI-powered tools will be able to leverage advanced machine learning techniques to mitigate emerging threats, perform real-time threat intelligence, and quickly respond to cyber threats.
Adopting a more proactive cybersecurity stance and modern mitigation tactics will help healthcare thwart attacks. As the healthcare industry awaits the fallout of the Change Healthcare breach, the ripple effects could be a catalyst for change, providing motivation for healthcare providers to arm themselves with more modern, robust threat protection systems and tactics.
 About Troy Hawes
About Troy Hawes
Troy is a managing director with the Cybersecurity Consulting practice at Moss Adams and has been providing IT consulting services since 2001. Troy serves clients in a variety of industries including communications and media, technology, health care, and higher education. He is adept at working with the specialty IT compliance and security needs of hospitals and providers, private businesses, government and tribal entities. Troy is a frequent speaker and highly published thought leader on IT compliance and cybersecurity topics.
< + > Zephyr AI Raises $111 Million in Series A Financing
Latest Investment Will Support the Democratization of Precision Medicine Through the Advancement of Novel Explainable AI Algorithms
Zephyr AI, Inc. (Zephyr AI), a healthcare technology company committed to developing fast and explainable Artificial Intelligence (AI) solutions to democratize precision medicine, today announced it has successfully closed a $111 million Series A funding round with participation from Revolution Growth, Eli Lilly & Company, Jeff Skoll, and EPIQ Capital Group, among others. The company is developing improved data federation tools along with various machine learning algorithms in the areas of oncology and cardiometabolic disease.
“The US has the highest rate of avoidable cancer and cardiometabolic-related deaths among any high-income country. We must do better,” said Grant Verstandig, Zephyr AI’s Co-Founder and Executive Chairman. “At Zephyr AI, we are harnessing the power of AI to extract novel insights to better define patient stratification and response predictions as well as improve federation of real-world data. With our world-class team and the support of this investor group, we are deploying one of the largest clinicogenomic datasets that has unprecedented breadth across disease states and data partners. Collectively, we are now well positioned to support our mission of democratizing precision medicine, enhancing both the speed and success of clinical trials.”
According to Dr. Justin Stebbing, Chairman of Zephyr AI’s Scientific and Medical Advisory Board, Editor of Oncogene (published under the Nature portfolio), and Professor of Biomedical Sciences at ARU, Cambridge, the company’s technology stands out along two crucial dimensions. “First, it has empirically demonstrated the ability to navigate the intricacies of real-world patient data, historically a challenge in the field. Second, leveraging recent breakthroughs in representation learning, the technology elucidates the biological context underlying its predictions. This contextual understanding is pivotal in drug development decision-making, revealing patient selection insights unpredictable using today’s tools to maximize the value of both approved medicines and drugs in development.”
The new funds will enable Zephyr AI to further enhance its analytical speed and fortify its extensive collection of training and validation data sets. Moreover, the funds will support the expansion of the company’s scientific and commercial teams to expedite the delivery of its rapidly growing pipeline of insights to the market.
“The expansion of our diverse multimodal data resources will accelerate the advancement of Zephyr AI’s algorithms, paving the way for us to transform the landscape of precision medicine and improve outcomes for our partners and patients,” said Jeff Sherman, Co-Founder, Interim CEO, and Chief Technology Officer at Zephyr AI.
“We are excited to be part of this growing ecosystem of AI-enabled drug development and welcome the opportunity to attend AACR where we will engage with the scientific community and present some of our emerging scientific insights from our platform,” Sherman said.
Cooley LLP served as legal counsel for Zephyr AI.
About Zephyr AI
Zephyr AI is a high-growth healthcare technology company committed to radically reshaping precision medicine in oncology and cardiometabolic disease. Through partnerships and proprietary data, Zephyr AI is curating the world’s most comprehensive healthcare dataset and marrying it with cutting-edge artificial intelligence algorithms to generate novel, translatable insights to build tools and products that support patients and providers and fuel ongoing research. At Zephyr AI, our mission-focused team of world-class software engineers and biologists leverage big data and next-generation technology to derive transformational insights and build enduring partnerships that will revolutionize the treatment of cancer and cardiometabolic disease. Visit us at zephyrai.bio and follow us on LinkedIn.
Originally announced March 13th, 2024
Wednesday, April 24, 2024
< + > National University Hospital launching AI-driven digestive centre
< + > Patch management advice for fixing IoT vulnerabilities
< + > Hospitals Outside of US Investing in Portals and Digital Front Door According to Latest KLAS Report
The KLAS Research report on Global Patient Engagement 2024 found that healthcare organizations outside the US are investing in patient portals, digital front door experiences (self-scheduling and self check-in) and virtual care/patient monitoring.
Healthcare IT Today sat down with Everton Santos, Vice President of International at KLAS Research to hear his insights on this report.
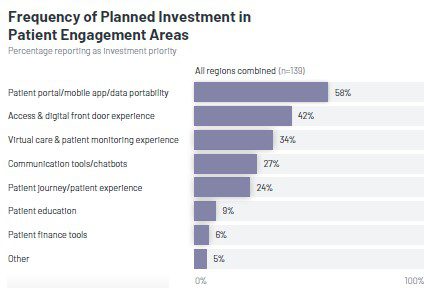 “What we found is that patients in those regions are hungry for an online platform where they can see, not only their lab results, but also their medical history, schedule an appointment, check-in for an appointment, and pay their bills,” explained Santos.
“What we found is that patients in those regions are hungry for an online platform where they can see, not only their lab results, but also their medical history, schedule an appointment, check-in for an appointment, and pay their bills,” explained Santos.
According to Santos, being more patient-centric is just becoming more prevalent in regions like the EU and Asia, which is why there is a desire to invest in technology for that purpose.
While doing the research for the report, Santos was surprised to learn how many healthcare organizations in emerging markets (Latin American, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East) were using WhatsApp to communicate with patients. This included confirming appointments, scheduling visits, and sending links to chatbots to gather information.
Watch the interview with Everton Santos to hear more of his insights from international healthcare markets.
Learn more about KLAS at https://klasresearch.com/
Listen and subscribe to the Healthcare IT Today Interviews Podcast to hear all the latest insights from experts in healthcare IT.
And for an exclusive look at our top stories, subscribe to our newsletter and YouTube.
Tell us what you think. Contact us here or on Twitter at @hcitoday. And if you’re interested in advertising with us, check out our various advertising packages and request our Media Kit.
< + > Leveraging AI to Address the Mental Health Crisis
The following is a guest article by Raj Tumuluri, Founder and CEO at Openstream.ai
As healthcare providers, you are acutely aware of the staggering mental health challenges facing our societies today. Depression, anxiety, PTSD, and suicidal ideation have reached pandemic levels, exacerbated by the relentless pace of modern life. From the general population to students in high-stress environments and frontline workers, a severe shortage of clinical personnel has created harrowing bottlenecks in accessing timely mental health evaluations and care.
The weight of this crisis calls for innovative solutions that can simultaneously reduce strain on overextended mental health professionals while expanding access to vital assessments. Fortunately, the rapid advancement of Conversational Artificial Intelligence (CAI) is poised to revolutionize how we approach mental health screenings and prioritize at-risk individuals for higher-level interventions.
At the forefront of this paradigm shift are Embodied Virtual Assistants (AI-powered avatars) and voice agents capable of engaging in naturalistic mental health assessments remotely by using multimodality, neuro-symbolic AI, and other rapidly evolving AI techniques and tools. Generating natural, human-like conversations with patients is much more than an ability to robotic scripted dialogues. Conversational AI mental health agents can engage in empathetic, natural conversations with end-users. As is the case with their human counterparts, these agents are effective communicators with the ability to observe, understand, and engage at many levels by employing various nuances of human conversation. They accomplish this through the use and understanding of facial expressions, voice intonation, and a variety of other non-verbal cues such as gestures or eye-gaze in tandem.
Powered by machine learning models trained on vast datasets, these AI agents can conduct interviews in any language, analyze responses, and identify potential mental health risks with increasing accuracy. Their consistent availability and scalability allow for broad deployment, drastically reducing wait times and access to help for individuals who otherwise may go underserved.
Already, pilot programs leveraging avatar-based assessments have demonstrated remarkable potential. Individuals can complete evaluations from the comfort of their homes or private spaces, fostering an environment conducive to open and honest disclosure. Perceived as lacking overt judgment, these AI avatars can potentially encourage more candid responses than conversations with human clinicians.
For students navigating academic pressures, first responders facing accumulated trauma, and military personnel pre- and post-deployment, these AI solutions present an opportunity for low-barrier mental health screening. Assessments can be easily integrated into existing protocols, ensuring no one slips through the cracks due to scheduling conflicts or resource constraints.
Moreover, these AI systems’ affordability and force multiplication capacity are pivotal advantages. A handful of human experts can effectively monitor and calibrate multiple AI agents, maximizing clinical bandwidth. This synergistic human-AI collaboration model reserves in-person psychologist and psychiatrist time for complex cases while also enabling AI-led triage and preliminary assessments at scale.
The exponential growth of data collected through these AI assessments also holds profound potential for advancing our understanding of mental health. Robust analytics and pattern recognition could yield insights into risk factors, environmental stressors, and demographic susceptibilities – informing public policy, institutional support frameworks, and preventative intervention strategies.
As an illustration, the UK’s current post-deployment mental illness screening costs approximately £34 per partial assessment. AI solutions could consolidate multiple evaluations into a unified, holistic screening protocol without substantially increasing personnel costs. Conditions like PTSD, suicidal risk, and postpartum depression could be seamlessly integrated, enhancing our ability to proactively identify and assist those in need.
Of course, the integration of AI into such a sensitive domain is not without ethical considerations. Preserving data privacy, mitigating algorithmic biases, and ensuring human oversight are paramount. Multidisciplinary collaboration between healthcare providers, computer scientists, ethicists, and policymakers will be crucial in developing robust governance frameworks that uphold the highest standards while unlocking AI’s potential.
Yet, the benefits of these conversational AI technologies are too compelling to ignore amidst our current mental health crisis. By intelligently augmenting our human resources with AI capabilities, we can drastically expand our screening capacities while reducing the burden on overtaxed mental health professionals. This force multiplication empowers us to be more proactive, identify risks earlier, and prioritize our human interventions where they are most urgently needed.
No technological solution can single-handedly resolve the deeply-rooted societal challenges contributing to mental health issues. However, AI-driven assessments represent a powerful tool in our arsenal – one that can elevate our screening efficacy, optimize our resource allocation, and ensure that no one’s cry for help goes unanswered or unheard.
Healthcare providers must eagerly embrace the responsible implementation of conversational AI. It is only through the harmonious convergence of human empathy and technological innovation that we can truly confront the silent pandemic eroding our mental health on a global scale.
 About Raj Tumuluri
About Raj Tumuluri
Raj is an inventor and one of the pioneers in multimodal AI with 20+ years of experience in building context-aware, multimodal, and mobile technologies; principal architect & evangelist of Openstream’s product vision & strategy; Co-Author of several books and W3C standards.
< + > This Week’s Health IT Jobs – April 24, 2024
It can be very overwhelming scrolling though job board after job board in search of a position that fits your wants and needs. Let us take that stress away by finding a mix of great health IT jobs for you! We hope you enjoy this look at some of the health IT jobs we saw healthcare organizations trying to fill this week.
Here’s a quick look at some of the health IT jobs we found:
- Medical Billing Manager – PrimeCare Managers
- Executive Director Memory Care Administrator – Lenity Management
- EHR Integration Architect – MEDITECH
- Senior MEDITECH Consultant WFH – HCA Healthcare
- Software Support IT Specialist – Magic Touch Software, Intl.
- Manager, Informatics – Clinical Terminologies – Oracle
- EMR Analyst – Clinical Documentation – Rochester Regional Health
- Medical Office Administrator – Biltmore Associates in Psychiatry
- Clinical Implementation Specialist – Fresenius Kabi USA
- IT Director – Insight Global
- Medical Coding and Billing Specialist – Associated Pediatricians
- MEDITECH Expanse Education Support Team – CereCore
- Accounting Specialist, Cash Management – MEDITECH
- Technical Project Manager (Healthcare/Health IT) – Themesoft Inc.
- IT Systems Specialist – Lyra Health
- Meditech Clinical Documentation Specialist – Mediant Health Resources
- Network Reimbursement Analyst – Blue Cross & Blue Shield of Mississippi
- Healthcare Technology Director – Renovo Solutions
- Billing Coordinator – Spruce Psychiatric Associates
- IT Process Manager – Midland Memorial Hospital
If none of these jobs fit your needs, be sure to check out our previous health IT job listings.
Do you have an open health IT position that you are looking to fill? Contact us here with a link to the open position and we’ll be happy to feature it in next week’s article at no charge!
*Note: These jobs are listed by Healthcare IT Today as a free service to the community. Healthcare IT Today does not endorse or vouch for the company or the job posting. We encourage anyone applying to these jobs to do their own due diligence.
< + > Bonus Features – March 1, 2026 – NVIDIA finds 70% of healthcare orgs use AI, insider breaches cost healthcare 48% more than other industries, plus 19 other stories
Welcome to the weekly edition of Healthcare IT Today Bonus Features . This article will be a weekly roundup of interesting stories, product ...
-
As I’m sure you know, times are tough. Wages have largely remained the same while prices have risen across the board – and healthcare is no ...
-
Solution Erases Long Phone Holds for Patients, Supports Overwhelmed Medical Front Desk Workers, and Improves Patient Access to Physicians A...
-
Announcement written by Zack Kanter, Founder and CEO at Stedi In February of last year, I gathered our engineering team in a war room. Chan...
